In this article
In a world where digital is everywhere from government to small business to individual consumers, cyber security has never been more important. Australia is like many other countries navigating a complex and ever-changing digital threat landscape. The Australian Signals Directorate’s (ASD) 2023 Cyber Threat Report is a must read; it shines a light on the challenges Australia faces in cyberspace.
This report is a snapshot of the current state of cyber security in Australia and a roadmap for the way forward in a sea of threats. It’s a year’s worth of data, insights and trends, the hard realities and the resilience of Australian businesses in the face of increasing cyber threats.
From state sponsored cyber espionage to profit driven cybercriminals the report highlights the many faces of the threats at Australia’s digital doorstep.
In this blog we’ll break down the key findings from the report, we’ll unravel the complexity of the threats Australia faces and look at the strategies the Australian Signals Directorate (ASD) are implementing. We’ll explore the importance of staying informed, prepared and resilient in a world where cyber threats loom large over our connected world.
For a comparison to last year’s key findings see TechBrain’s analysis of the ACSC 2022 cyber threat report.
The Current State of Australian Cyber Security in 2023
The Australian Signals Directorate’s (ASD) 2023 Cyber Threat Report shows a landscape of increasing complexity and intensity of threats, so cyber security teams need to be more vigilant and proactive.
Cyber Security Incidents are on the Rise
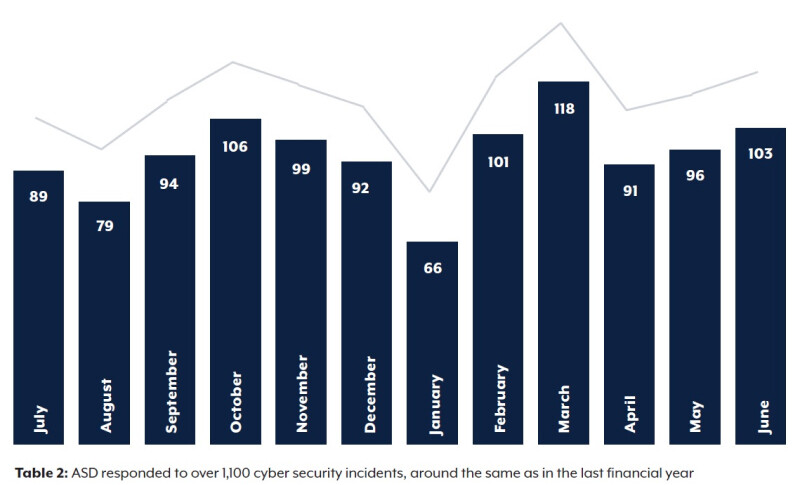
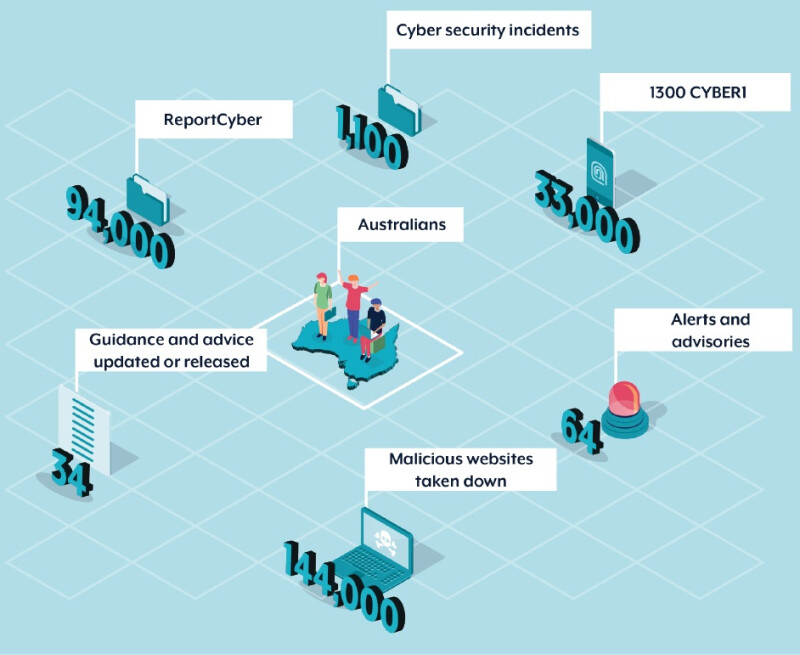
2022-23 has been a busy year for cyber activity against Australian interests. The Australian Signals Directorate (ASD) responded to over 1,100 cyber security incidents. That’s a big number that highlights the scale and frequency of the threats we face in the digital world.
These incidents range from targeted attacks by state sponsored actors to opportunistic breaches by cybercriminals exploiting vulnerabilities in systems.
The Threats are Getting More Complex
State actors are now engaging in cyber espionage, targeting critical infrastructure and government data. It’s not just about immediate gain but long-term positioning and intelligence gathering.
At the other end of the spectrum, cybercriminals are adapting to exploit new vulnerabilities and maximise financial gain. From ransomware attacks that lock businesses out of their own systems to sophisticated business email compromise schemes, the tactics are getting more complex and damaging.
Data Breaches are a Persistent Threat
Big data breaches like the one in September 22’ Optus breach has exposed millions of Australians’ personal information. These breaches not only compromise individual privacy but also wider risks like identity theft and fraud. The report highlights the need for robust data protection and quick incident response to mitigate the impact of these breaches.
The Patching Conundrum
One of the biggest problems with patching is the need for speed. When a vulnerability is disclosed, the clock starts ticking. The window between a vulnerability being disclosed and a cybercriminal exploiting it is getting smaller and the report found one in five critical vulnerabilities were exploited within 48 hours of a patch being available. This urgency clashes with the reality of deploying patches across complex networks.
Organisations must navigate a world where the need for rapid patching is at odds with practicalities and resource constraints. The future of patch management is about developing smarter, more efficient strategies, building a security aware culture and having the right mix of skills, automation and risk management techniques.
Cyber Security Trends and Threats
The report highlights several concerning trends. State actors are now targeting critical infrastructure to steal data and disrupt business. This is a major risk to national security and the economy. Meanwhile cybercriminals are getting more sophisticated and causing harm to Australian businesses.
Critical Infrastructure
State sponsored actors are aggressively targeting and breaching critical infrastructure sectors including energy, telco and finance. This is a big shift in the threat landscape from data theft to disruption of national assets.
These attacks are not just about stealing sensitive info but planting the seeds for future disruption or sabotage, a major threat to national security and public safety.
Espionage and Geopolitics
The report shows how these state sponsored activities often align with broader geopolitical agendas. Espionage is a key motivator with foreign governments seeking economic, political and technological advantage. The more connected the world is the worse these risks get, so international cooperation is key to identifying and countering these threats.
Ransomware
One of the biggest trends is the explosive growth of ransomware. Cybercriminals have refined their ransomware tactics, targeting big business and the public sector.
These attacks aren’t just about encrypting data; they’re increasingly about threats to release sensitive information publicly, known as ‘double extortion’. The disruption caused by these attacks can bring essential services to a standstill, resulting in big financial losses and loss of public trust.
Business Email Compromise (BEC)
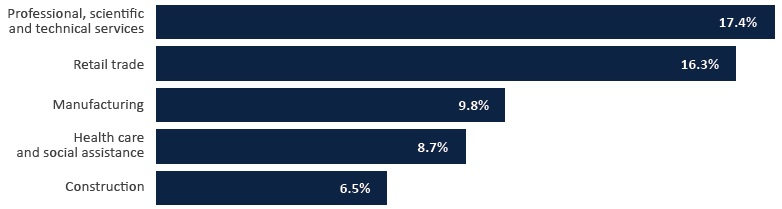
Business Email Compromise (BEC) has become a highly sophisticated form of cybercrime. Cybercriminals are now using more advanced social engineering to impersonate senior executives or trusted partners, tricking employees into transferring money or revealing sensitive information. The impact of these attacks can be catastrophic for small to medium sized businesses who don’t have the resources to recover from the losses.
Cybercrime Financial Impact 2023
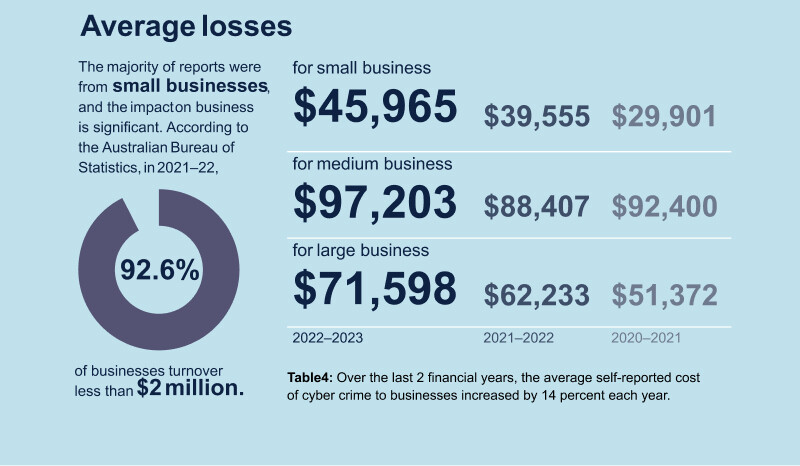
In 2023 the financial impact of cybercrime on Australian businesses and individuals reached record highs, it’s a big problem for the economy. The ASD 2023 Cyber Threat Report shows some alarming numbers: small business faced an average cost of $45,965 per cybercrime, medium business $97,203 and large business $71,598.
This is due to the increasing sophistication and frequency of cyber-attacks, including ransomware, business email compromise and online fraud. The 23% increase in cybercrime and nearly 94,000 reports (one every 6 minutes) is putting more pressure on the economy.
And the average cost of cybercrime has increased 14% which shows the scope and severity of these incidents is getting bigger. This financial impact not only affects the immediate financial health of businesses and individuals but also the long-term trust and investment in the digital economy, so we need to have robust cyber defence strategies and more awareness of cyber threats.
Response and Actions by the ASD
The Australian Signals Directorate (ASD) has been at the forefront of responding to and mitigating the many cyber threats outlined in the 2023 Cyber Threat Report. Their actions and strategies are key to national cyber security and resilience.
ASD’s international work, particularly in exposing threats like Russia’s Federal Security Service’s use of Snake malware, shows their commitment to global cyber security.
REDSPICE
REDSPICE (Resilience, Effects, Defence, Space, Intelligence, Cyber and Enablers) is a major strategic initiative by the Australian Signals Directorate to strengthen Australia’s cyber defence. This program will help the nation detect, deter and respond to many cyber threats.
It’s a multi-faceted approach that includes expanding cyber threat intelligence sharing, securing critical infrastructure and national incident response capabilities. REDSPICE is proof the ASD is adapting and evolving to the changing global cyber landscape so Australia remains at the forefront of cyber resilience and defence.
Cyber Security Partnership Program
The ADS runs the Cyber Security Partnership Program and has over 110,000 organisations and individuals from government, industry, academia and the private sector.
It’s to create a collaborative environment by sharing critical cyber threat intelligence and best practices to have a unified approach to cyber defence. Participants can access vital information, tools and resources to help them proactively identify and respond to cyber threats.
The program shows the importance of partnership and collaboration in cyber security, recognising that collaboration is key to countering the sophisticated and ever-changing cyber threats of the world.
Advocating for Better Cyber Awareness
At the heart of this is promoting the Australian Signals Directorate’s Essential 8, a set of strategies to mitigate cyber security incidents. The Essential 8 is a foundation framework that organisations can adapt and apply to their environment and risk profile.
These strategies include application whitelisting, patching applications, configuring Microsoft Office macro settings, user application hardening, restricting administrative privileges, patching operating systems, multi-factor authentication and regular backups.
Implement these and you’ll be more resilient to many cyber threats – external attacks and internal vulnerabilities. The Essential 8 is a guide to cyber security best practice and a reminder to have a layered approach to digital infrastructure.
Building a Cyber-Resilient Australia
As we look towards the future, it’s evident that building a cyber-resilient Australia is a dynamic and collaborative effort. The threats may be evolving, but so are our strategies and resources. By staying informed, proactive and united in our approach to cyber security, businesses can navigate this digital era with confidence and resilience.
By utilising TechBrain’s sophisticated cyber security capabilities developed by in-house specialists committed to our national cybersecurity, you can enhance your business’s cyber security posture and face digital threats head-on.