In this article
A cyber security risk register is a vital tool for organisations to identify, assess and manage potential cyber threats. This centralised document lists all identified risks, their likelihood of occurrence, potential impact and the measures in place to mitigate them.
By maintaining a well-structured risk register, organisations can proactively address cyber risks and minimise their exposure to potential cyber attacks.
Implementing a cyber risk register offers several key benefits:
Enhanced visibility:
A cyber risk register provides a clear and comprehensive overview of an organisation’s cyber risk landscape. By consolidating all identified risks in one place, stakeholders can easily understand the scope and nature of the threats facing their organisation.
This enhanced visibility enables better communication and collaboration among teams, facilitating a shared understanding of the risks and the necessary actions to mitigate them.
Strategic prioritisation:
With limited resources and competing priorities, organisations must focus their efforts on the most critical risks.
A well-maintained risk register allows organisations to prioritise risks based on their risk category and potential impact. By assigning risk ratings and categorising risks based on severity, organisations can ensure that the most significant threats receive the attention and resources they require.
Informed decision-making:
A cyber risk register provides stakeholders with the data and insights needed to make informed decisions regarding risk management.
By quantifying risks and assessing their potential impact on the organisation, stakeholders can evaluate the costs and benefits of different mitigation strategies. This data-driven approach identifying cyber security risks enables organisations to allocate resources effectively, balancing the need for security with operational efficiency and business objectives.
Regulatory compliance:
Many industries are subject to specific cyber security regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, the My Health Record regulation or Essential 8 in Australia.
Maintaining a cyber risk register demonstrates an organisation’s due diligence in identifying and managing risks, supporting compliance with relevant regulations. By aligning the risk register with regulatory requirements, organisations can ensure they are meeting their legal obligations and avoiding potential penalties.
Continuous improvement:
Cyber threats are constantly evolving and organisations must adapt their risk management strategies accordingly. A cyber risk register facilitates regular review and updates, allowing organisations to keep pace with changing threats.
By continuously monitoring the risk landscape, reassessing the effectiveness of mitigation measures and incorporating lessons learned from incidents, organisations can refine their approach to risk management and improve their overall cyber security posture.
Understanding Cyber Security Risks
At its core, a cyber security risk is any potential threat that could compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of an organisation’s information systems, data, or networks. These risks are diverse and can originate from a wide range of sources, including malicious actors, system vulnerabilities, human error, or even natural disasters.
By recognising the different types of cyber security threats and their potential impact on your organisation, you can better appreciate the importance of maintaining a comprehensive cyber risk register as a key component of your overall risk management strategy.
Common Cyber Risks
Data breaches:
Unauthorised access to sensitive information, such as customer data or intellectual property.
Malware:
Malicious software designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorised access to computer systems.
Phishing:
Fraudulent attempts to deceive individuals into revealing sensitive information or installing malware.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks:
Overloading systems or networks to render them unavailable to users.
Insider threats:
Risks posed by employees, contractors, or partners with access to sensitive information.
Business leaders should remain vigilant to potential threats cyber security risks can have on their business, potentially leading to significant financial losses, damage to reputation and customer trust, legal and regulatory repercussions, loss of intellectual property and competitive advantage and prolonged operational disruptions that can hinder productivity and growth.
Steps to Create a Cyber Security Risk Register
Creating a comprehensive cyber security risk register involves several key steps to ensure that all potential risks are identified, assessed and addressed effectively.
Identify Assets & Vulnerabilities
The first step in creating a risk register is to identify the organisation’s critical assets, such as hardware, software, data and networks. This process involves conducting a thorough inventory of all IT assets and determining their value to the organisation.
Once the assets are identified, the next step is to pinpoint vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cyber threats. This can be achieved through vulnerability assessments, penetration testing and regular security audits.
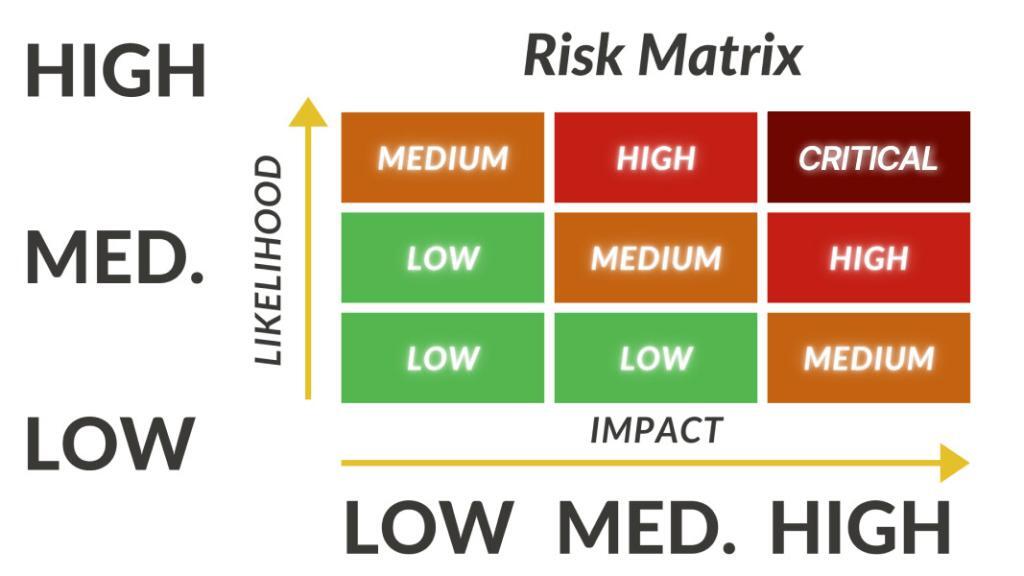
Assess Risk Probabilities
After identifying assets and vulnerabilities, the next step is to use a risk matrix to assess the likelihood of each risk occurring. This involves analysing the probability of a threat exploiting a specific vulnerability and the potential impact on the organisation.
Factors to consider when assessing risk probabilities include the risk owner, current threat landscape, the effectiveness of existing security controls and the attractiveness of the organisation as a target for cybercriminals.
Prioritise Risks Based on Severity
With the risk probabilities assessed, organisations can prioritise risks based on a risk priority scale. Risks with a high probability and significant potential impact should be given top priority, while those with lower probabilities and less severe consequences can be addressed later.
Prioritising risks helps organisations allocate resources effectively and ensures that the most critical operational risks are addressed first.
Develop Risk Mitigation Strategies
Once risks have been prioritised, the next step is to develop appropriate mitigation strategies. These strategies may include implementing new security controls, updating existing ones, or creating incident response plans.
The goal is to reduce the likelihood of a risk occurring or minimise its impact if it does occur. Mitigation strategies should be tailored to the specific risks and align with the organisation’s overall security posture and business objectives.
Assign Ownership & Responsibilities
To ensure that risk mitigation strategies are implemented effectively, it is crucial to assign ownership and responsibilities. Each risk should have a designated owner who is responsible for overseeing the implementation of mitigation measures and monitoring their effectiveness.
Additionally, roles and responsibilities should be clearly defined for all stakeholders involved in the cyber security risk assessment and risk management process, including IT staff, management and end-users. This ensures accountability and helps maintain a proactive approach to managing cyber risks.

Best Practices for Maintaining a Risk Register
After creating a comprehensive cyber risk register, it’s essential to maintain its effectiveness over time. Just as the digital landscape and the threats within it continue to evolve, so too must your risk register adapt to remain a relevant and powerful tool in your organisation’s cyber risk management strategy.
Implementing best practices for maintaining your cyber security risk register ensures that it continues to provide accurate, up-to-date information and enables your organisation to stay ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
By dedicating time and resources to cyber security compliance standards and regularly updating and refining your risk register, you can foster a proactive, resilient approach to managing cyber risks and safeguarding your organisation’s critical assets and reputation.
Engage Key Stakeholders
Engage IT staff, management, legal teams and other relevant departments in the risk identification and assessment process. Collaboration ensures all potential risks are considered and the register reflects the organisation’s collective knowledge.
Alignment With Business Objectives
Align the risk register with overall business objectives, considering the impact of cyber risks on operations, reputation, financial performance and compliance. Prioritise mitigating cyber risks based on their potential to disrupt or hinder the achievement of these goals.
Regular Reviews, Updates & Stakeholder Feedback
Conduct regular reviews and updates to reassess the likelihood and impact of identified risks and identify new risks. Solicit feedback from stakeholders to gauge the effectiveness of mitigation strategies and identify areas for improvement.
Automation Tools
Utilise automation tools, such as risk assessment software, vulnerability scanners and incident response platforms, to streamline the risk management process, ensure consistency and improve accuracy. Choose tools that integrate well with existing systems and provide necessary customization and control.
Adhering to these best practices helps organisations maintain an effective cyber risk register, make informed decisions about risk mitigation strategies, allocate resources effectively and improve overall cyber resilience.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Implementing and maintaining an effective cyber risk register can present various challenges for organisations. Here are some common obstacles and strategies to overcome them.
Lack of Resources or Expertise
One of the most significant challenges organisations face is a lack of resources or expertise to create and maintain a comprehensive risk register. Smaller organisations may not have dedicated cyber security staff or the budget to hire external consultants.
- Investing in training and education for existing IT staff to develop in-house expertise.
- Collaborating with industry peers or joining cyber security forums to share knowledge and best practices.
- Exploring cost-effective solutions, such as open-source risk assessment tools or managed security providers.
- Prioritising the most critical risks and focusing resources on addressing those first.
Difficulty in Quantifying Risks
Quantifying the likelihood and potential impact of cyber risks can be challenging, as it often involves estimating the probability of future events and their consequences.
- Use a consistent risk assessment framework that defines clear criteria for likelihood and impact ratings.
- Leverage industry benchmarks, threat intelligence and historical data to inform risk assessments.
- Engage stakeholders from different departments to provide diverse perspectives on potential impacts.
- Use risk assessment tools that provide guidance and templates for quantifying risks.
Resistance to Change or Adoption
Implementing a cyber risk register may require changes to existing processes, which can be met with resistance from employees or stakeholders.
- Communicate the benefits of the risk register and how it aligns with organisational goals.
- Involve stakeholders in the development process to foster a sense of ownership and buy-in.
- Provide training and support to help employees understand their roles and responsibilities.
- Celebrate successes and share positive outcomes to reinforce the value of the risk register.
Balancing Risk Mitigation with Business Needs
Mitigating cyber risks often involves implementing various security measures or controls that may impact business operations or user experience.
- Prioritise risks based on their potential impact and align mitigation strategies with business objectives.
- Engage business stakeholders in the cyber risk assessment process to understand their needs and constraints.
- Consider the total cost of ownership for mitigation strategies, including the cost of potential business disruptions.
- Regularly review and adjust mitigation strategies to ensure they remain effective and aligned with business needs.
By proactively addressing these common challenges, organisations can overcome obstacles and establish a robust cyber risk register that effectively supports their cyber security efforts.
Remember that building a strong risk management culture takes time and requires ongoing commitment from leadership and employees alike.
Create a Secure Future with Minimal Cyber Risk
In today’s digital landscape, a comprehensive cyber security risk register is essential for proactively identifying, assessing and managing potential risks. By prioritising risks based on likelihood and impact, allocating resources effectively and making informed decisions, you can significantly reduce your organisation’s exposure to cyber threats.
We encourage you to start creating your own cyber security risk register using the best practices discussed in this blog post. To help you get started, we’ve created a TechBrain branded risk register template that you can download and customise to fit your organisation’s specific needs.
Building a robust risk management culture requires ongoing commitment and collaboration from all levels of your organisation. Stay vigilant in identifying cyber security threats, regularly review and update your risk register and engage stakeholders in the process to create a more secure future for your business.
At TechBrain, we’re committed to helping organisations navigate the complex world of cyber security. If you need further guidance on creating and maintaining an effective cyber security risk register, meeting cyber security compliance standards or managing your cyber security end-to-end don’t hesitate to reach out to our team of experts.
Start taking control of your cyber risks today and create a secure future for your organisation with TechBrain.