In this article
When seeking to understand the value of a cyber security certification you need to understand the risks of non-compliance. Data breaches, system failures, reputational damage and financial losses are all too present cyber dangers for Australian businesses.
Knowing your business is up to standard is key, which is why we’ll explore the key components of an information security management system (ISMS) and how it can help your business stay secure and resilient in the face of evolving cyber threats, specifically through the internationally recognised ISO 27000 series certification.
The ISO 27000 family of standards, developed by the International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), offers a comprehensive framework for establishing, implementing, and maintaining an effective Information Security Management System (ISMS).
By adopting these standards, businesses can gain the confidence and security they need to thrive in the digital age, knowing that their sensitive information assets are well-protected against evolving cyber threats.
What is an Information Security Management System (ISMS)?
An information security management system (ISMS) is a complete strategy to manage the information security threats inside a company.
Information security management systems encompass a set of policies, procedures and controls that are designed to protect the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information assets while aligning with the organisation’s business objectives, legal and regulatory requirements.
The key components of an ISMS
Policies and procedures
Documented guidelines that define how information security is managed within the organisation, including roles and responsibilities, acceptable use policies and incident response plans.
Risk management
A systematic process for identifying, assessing, and treating information security risks, taking into account the organisation’s specific context and risk appetite.
Asset management
Identification, classification, and protection of the organisation’s information assets, including hardware, software, data, and intellectual property.
Access control
Ensuring that only authorised individuals have access to sensitive information and systems is based on the principle of least privilege.
Incident management
Procedures for detecting, responding to and recovering from information security incidents, such as data breaches or system failures,.
Business continuity
Plans and procedures for guaranteeing, in the case of a disturbance or disaster, the continuous availability of important information systems and services.
Compliance
Policies for making sure the information security procedures of the company follow industry standards and best practices as well as relevant legal and regulatory standards.
The Business Case for Implementing an ISMS
Investing in an ISMS is not just a matter of compliance or risk management; it also makes good business sense. From gaining a competitive advantage and enhancing customer trust to improving operational efficiency and reducing the costs associated with security incidents, the business case for implementing an ISMS is clear and compelling.
Competitive advantage
Demonstrating a commitment to information security can help an organisation differentiate themselves from their competitors and win the trust of customers and partners who value the protection of their sensitive data.
Improved efficiency
An ISMS can help streamline and standardise information security processes, reducing duplicate effort and enabling more effective use of resources.
Enhanced decision-making
By providing a clear picture of an organisation’s information security risks and the effectiveness of its controls, an ISMS can support better-informed decision-making at all levels of the business.
Reduced costs
While implementing an ISMS requires a significant initial investment, it can ultimately provide an effective hedge against the significant costs associated with security incidents, such as lost productivity, legal fees and reputational damage.
Increased resilience
An ISMS can help businesses prepare for and respond to information security incidents more effectively, minimising the impact on operations and ensuring the ongoing availability of critical systems and services.
Managing information technology best practices is essential for ensuring compliance with ISO 27001 standards and protecting sensitive data across various industries.
Organisations must adhere to the Australian Privacy Principles (APPs) under the Privacy Act 1988, which sets out standards for the collection, use, disclosure and storage of personal information. In the healthcare sector, the My Health Records Act 2012 establishes requirements for the privacy and security of electronic health information.Financial institutions must comply with the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) Prudential Standard CPS 234, which focuses on information security management.
By aligning their practices with ISO 27001 and these industry-specific regulations, businesses can showcase their commitment to information security, maintain compliance and build trust with their customers and stakeholders.
Real-world examples of successful ISMS implementations, such as those at Fujitsu, demonstrate the tangible benefits that businesses can realise by adopting an ISO 27001-compliant approach to information security.
ISMS Frameworks and Security Controls
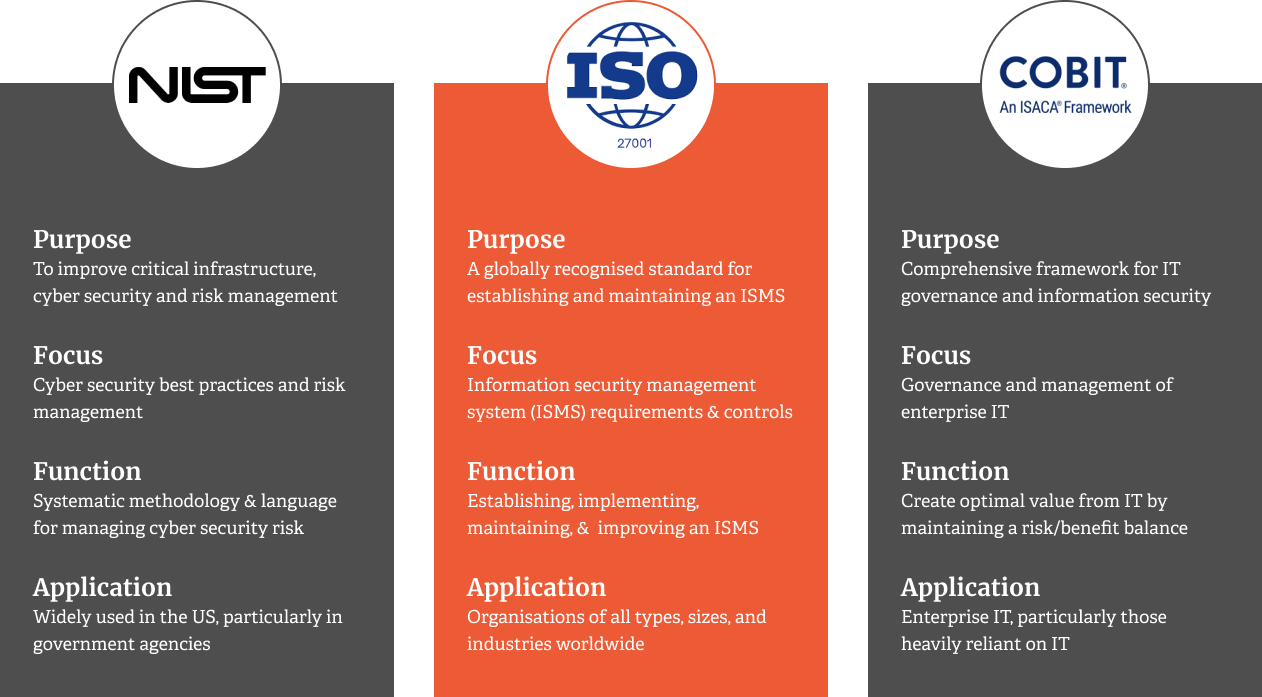
Several ISMS frameworks have been developed to guide organisations in implementing and managing their information security practices. Some of the most popular frameworks include:
ISO 27001
The international standard for ISMS provides a comprehensive set of requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an ISMS.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
A voluntary framework was developed by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology to help organisations manage and reduce cybersecurity risk.
COBIT
A framework for IT governance and management, including information security aspects, was developed by ISACA.
At the core of these frameworks are information security controls, which serve as safeguards or countermeasures specifically designed to protect the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information assets from unauthorised access, modification or disclosure.
These security controls can be categorised into three main types:
- Administrative controls are policies, procedures, and guidelines that define how information security is managed within an organisation.
- Technical controls: hardware, software and network mechanisms that protect information assets from unauthorised access or modification.
- Physical controls: measures that protect physical assets, such as data centres, servers, and workstations, from theft, damage, or unauthorised access.
It’s also important to consider the physical and environmental security controls necessary for protecting physical areas, equipment and facilities from interventions.
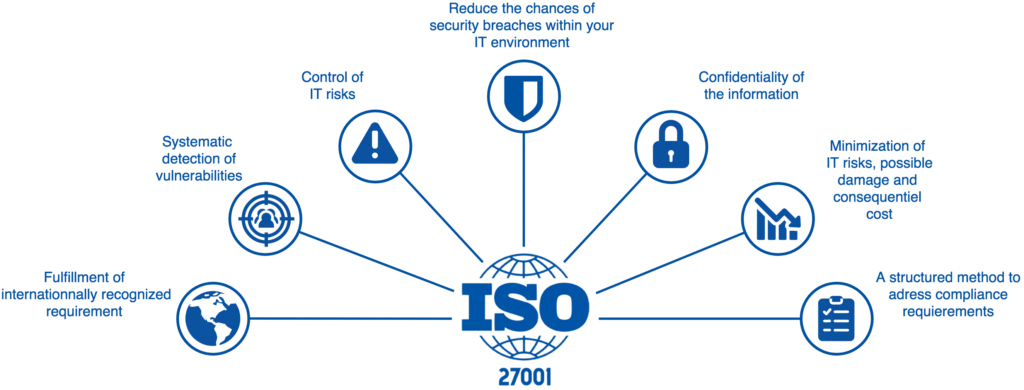
The ISO 27000 Family of Standards
The ISO/IEC 27000 family of standards provides a comprehensive framework for implementing an ISMS, with each standard focusing on a specific aspect of information security management. The most relevant standards for businesses are:
ISO 27001
The flagship standard of the ISO/IEC 27000 series provides the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an ISMS.
ISO 27002
A code of practice that provides guidelines and best practices for implementing the security controls outlined in ISO 27001.
ISO 27003
Guidance on the implementation of an ISMS, including the planning, design and implementation phases.
ISO 27004
Guidelines for monitoring, measuring, analysing and evaluating the effectiveness of an ISMS.
ISO 27005
Guidelines for information security risk management, including cyber risk assessment and risk treatment.
ISO 27006
Requirements for bodies providing audits and certifications of ISMS, ensuring consistency and credibility in the certification process.
ISO 27007
Guidelines for conducting ISMS audits that help organisations assess the conformity of their ISMS with the requirements of ISO 27001.
By understanding the scope and purpose of each standard, businesses can navigate the ISO/IEC 27000 landscape more effectively and select the standards that are most relevant to their specific cyber security needs and objectives.
Implementing an ISO 27001-compliant ISMS
Implementing an ISMS compliant with ISO 27001 is a detailed process that involves defining boundaries and objectives, securing management support and resources, establishing a project team, conducting risk assessment, selecting and implementing security controls, documenting policies, procedures, records, monitoring effectiveness and continually improving.
While the specific steps may vary depending on the organisation’s size, industry and risk profile, the following roadmap provides a general guide to the key stages of ISMS implementation:
- Scoping and planning: define the boundaries and objectives of the ISMS, secure management support and resources and establish a project team and governance structure.
- Risk assessment: identify, analyse and evaluate the organisation’s information security risks, taking into account the business context, legal and regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations.
- Control selection and implementation: Select and implement appropriate security controls based on the results of the risk assessment, taking into account the organisation’s risk appetite and available resources.
- Documentation and communication: Develop and maintain the policies, procedures, and records required to support the ISMS, and communicate the ISMS objectives and requirements to relevant stakeholders.
- Monitoring and review: Establish processes for monitoring and measuring the effectiveness of the ISMS, conducting internal audits and management reviews, and identifying opportunities for improvement. It is crucial to incorporate information security incident management to handle, communicate, resolve, and prevent the recurrence of security incidents.
- Continual improvement: Regularly review and update the ISMS based on changes in the business environment, emerging risks and opportunities, and feedback from stakeholders.
By following this roadmap and leveraging the guidance provided by the ISO 27000 standards, businesses can implement an ISMS that is tailored to their specific needs and enables them to manage their information security risks more effectively.
Benefits of Working with an ISO 27001 Specialist
For businesses without internal expertise or resources, implementing an ISO 27001-compliant ISMS can be a challenging undertaking. That’s where experienced ISO 27001 specialists like TechBrain can add significant value during the ISMS audit phase.
Expert guidance
ISO 27001 specialists have in-depth knowledge of the standard and its implementation and can provide expert guidance and support throughout the ISMS journey.
Accelerated implementation
By leveraging proven methodologies and best practices, ISO 27001 specialists can help businesses implement an ISMS more quickly and efficiently, reducing the time and cost involved.
Reduced risk
Our team can help identify and mitigate information security risks more effectively, reducing the likelihood and impact of security incidents. They also emphasise the importance of managing supplier relationships to ensure that suppliers and partners adhere to information security controls.
Ongoing support
We provide ongoing support and guidance to help businesses maintain and improve their ISMS over time, ensuring that it remains relevant and effective in the face of evolving risks and challenges.
By working with an ISO 27001 specialist, businesses can navigate the complexities of ISMS implementation more effectively and realise the benefits of a robust and resilient information security posture more quickly and efficiently.
Safeguard your Data and Protect your Reputation with ISO 27000
The ISO 27000 family of standards provides a comprehensive framework for establishing, implementing and maintaining an effective information security management system.
By adopting an ISO 27001-compliant ISMS, Australian businesses can protect their sensitive information assets, comply with legal and regulatory requirements, maintain customer trust and mitigate the risks and potential financial losses associated with cyber threats.
While implementing an ISMS can be a complex and challenging process initially, the benefits are clear and compelling. By partnering with an experienced ISO 27001 specialist like TechBrain, businesses can navigate the complexities of ISMS implementation more effectively and realise the benefits of a robust and resilient information security posture.